Digital Mental Health

Digital mobile sensing refers to the use of sensors and data from mobile devices (such as smartphones) to gather information about various aspects of users' behavior, activities, and environments. This approach leverages the capabilities of built-in sensors in mobile devices to collect data for a wide range of applications, including health monitoring, behavioral analysis, and context-aware services. Here are some key aspects of digital mobile sensing:
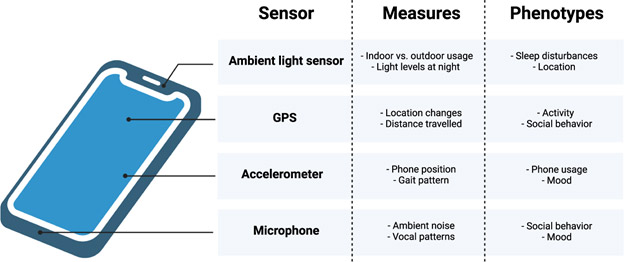
Mobile devices are equipped with a variety of sensors, including accelerometers, gyroscopes, GPS, cameras, microphones, ambient light sensors, and more. Each sensor provides unique information that can be used for different purposes.
Mobile sensing is often used for health-related applications. For example, accelerometers can track physical activity, GPS can provide location-based information, and heart rate sensors can monitor cardiovascular health. Mobile health (mHealth) apps utilize these sensors to offer personalized health insights.
Sensors can capture data related to users' behaviors. For instance, analyzing accelerometer data can reveal patterns of movement, and microphone data can be used to study speech patterns or ambient sounds. This information can be valuable for understanding and predicting user behavior.
Mobile sensing enables context-aware applications that adapt to users' surroundings. By collecting data on location, time, and environmental conditions, apps can provide relevant information or services based on the user's context.
Sensors on mobile devices can be used to monitor the environment. For example, light sensors can measure ambient light levels, and temperature sensors can provide information about the surroundings. This data can be valuable for both personal and research purposes.
As mobile sensing involves collecting data from users' personal devices, privacy is a significant concern. Developers and researchers must implement privacy-preserving measures to ensure that sensitive information is handled appropriately and users have control over their data.
Mobile sensing data is often used in research to gain insights into various phenomena. Researchers can collect and analyze large datasets to understand trends, correlations, and patterns in human behavior or health.
Digital mobile sensing has applications in diverse fields, including healthcare, psychology, urban planning, and human-computer interaction. While it offers numerous benefits, it's important to address privacy and ethical considerations to ensure responsible and secure use of personal data.
Digital mental health 360 continuous monitoring refers to the comprehensive and continuous monitoring of an individual's mental health using digital technologies. This approach involves the use of various tools and platforms to gather, analyze, and track data related to a person's mental well-being throughout their daily life. Here are some key aspects of digital mental health 360 continuous monitoring:
Wearables such as smartwatches or fitness trackers equipped with sensors can monitor physiological indicators like heart rate, sleep patterns, and activity levels. These data points can provide insights into the individual's overall well-being.
There are numerous mental health apps that allow users to self-report their mood, stress levels, and daily activities. These apps may also incorporate features like mood tracking, journaling, and reminders for self-care.
Beyond basic wearables, more advanced technologies can include monitoring biometric data like skin conductance, facial expressions, and voice tone to detect emotional states and potential signs of mental health issues.
Some platforms offer digital therapeutic interventions that leverage continuous monitoring data to provide personalized mental health support. These interventions may include cognitive-behavioral therapy exercises, mindfulness practices, or mood regulation techniques.
Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms can analyze the collected data to identify patterns, trends, or anomalies that may indicate changes in mental health. This can enable early intervention or personalized recommendations.
Given the sensitive nature of mental health data, ensuring robust privacy and security measures is crucial. Compliance with data protection regulations and the use of encryption are essential components of any digital mental health monitoring system.
Continuous monitoring in a 360-degree approach aims to provide a holistic view of an individual's mental health, allowing for proactive and personalized interventions. However, it's important to consider ethical and privacy concerns while implementing such technologies to protect the user's sensitive information and maintain trust in digital mental health solutions.
Behavioral and physical health integration refers to the collaborative and comprehensive approach to addressing both mental or behavioral health and physical health within the healthcare system. Traditionally, these two aspects of healthcare have been treated separately, but there is a growing recognition of the interconnectedness between mental and physical well-being. Integrating behavioral and physical health can lead to more holistic and effective healthcare delivery. Here are some key aspects of behavioral and physical health integration:
Integration recognizes that mental and physical health are interconnected and impact each other. Holistic patient care involves addressing both aspects to improve overall well-being.
Collaborative care models involve a team-based approach where healthcare professionals from different disciplines (e.g., physicians, psychologists, social workers) work together to address both behavioral and physical health needs.
Integrating behavioral and physical health often starts with comprehensive screening and assessment tools that can identify potential issues in both domains. This helps in early identification and intervention.
The biopsychosocial model considers biological, psychological, and social factors in understanding and treating health conditions. Integrative care embraces this model to address the multifaceted nature of health.
Effective communication and coordination among healthcare providers are crucial. Integration involves sharing relevant information between primary care physicians, specialists, and behavioral health providers to ensure a coordinated and cohesive care plan.
Encouraging patients to actively participate in their care decisions is a key principle of integration. This involves collaboration between patients and healthcare providers to set goals and make informed choices.
Training healthcare providers in both behavioral and physical health aspects enhances their ability to identify, understand, and address the complex interplay between mental and physical health.
Implementing integrated health information systems and technologies allows for the seamless exchange of information between behavioral health and physical health providers, improving care continuity.
Integrative care includes preventive measures and wellness programs that address lifestyle factors impacting both mental and physical health, promoting overall health and well-being.
Educating patients about the connection between mental and physical health and engaging them in their care can lead to better outcomes. This involves promoting health literacy and self-management skills.
Integrating behavioral and physical health is seen as a promising approach to address the complex healthcare needs of individuals. It recognizes that mental health conditions can impact physical health outcomes, and vice versa. This integrated approach aims to break down silos in healthcare delivery and improve the overall health and quality of life for individuals.